up transformer Explain with the Circuit Diagram A transformer designed to reduce the voltage from primary to secondary is called a step-down transformer. The transformation ratio of a transformer will be equal to the square root of its primary to secondary inductance (L) ratio. RELATED WORKSHEETS: Step-up, Step-down, and Isolation Transformers Worksheet In this video, Emma Dent will demonstrate how to use a step-up and step-down transformer. Step-up transformers boost the size of an alternating potential difference, while step-down transformers do the opposite, reducing it. You will need: 0-15V Laboratory Power Pack (AC Output) Digital Multimeters Wires and Crocodile Clips Transformer Coils Bulb Circuit - […] A boost converter (step-up converter) is a DC-to-DC power converter that steps up voltage (while stepping down current) from its input (supply) to its output (load). It is a class of switched-mode power supply (SMPS) containing at least two semiconductors (a diode and a transistor) and at least one energy storage element: a capacitor, inductor
Step-Up Transformer Simulation. A step-up transformer that increases the voltage from the primary winding to the secondary winding. The secondary winding consists of more turns than the primary winding. Step-up transformers are widely used in inverter and booster applications that convert low voltage to the desired high voltage. Circuit Diagram

Step Up Transformer: Definition, Working Principle (Step Up vs. Step Down) Circuit Diagram
Schematic diagram of the transformer. A schematic diagram of a step-up transformer is shown in image 2, wi th T 1 and T 2 representing the turns of the primary and secondary windings and V 1 and V 2 representing the in put and output voltages, respectively. The transformer's output winding is the secondary winding, whereas the primary winding is the transformer's input winding.
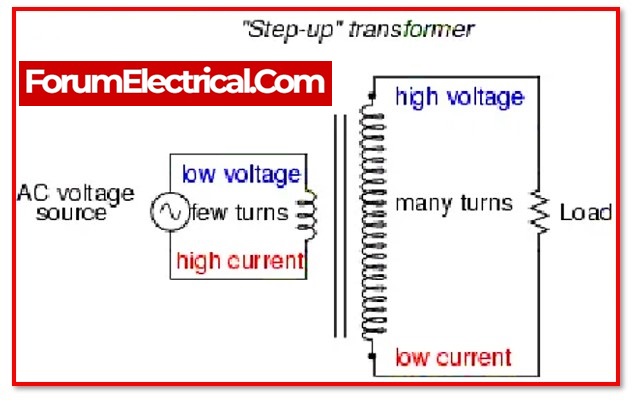
The step-up transformer gives the higher voltage as a output because the voltage is directly proportional to the number of turns in the windings. Hence, in a step up transformer with N 1 turns in primary winding, It increases or steps up the voltage in the output circuit. It decreases or steps down voltage in the output circuit. Effect on

Step Up Transformer: Definition, Diagram & Working Principle Circuit Diagram
Figure 1: step up transformer wiring diagram . What does a Step-up Transformer Do. Step-up transformers are used in electronic devices like inverters, batteries, and stabilizers to balance low and higher voltages in transformers. They are used in power transmission, playing a crucial role in transferring power to locations far from generating Step-down transformer: (many turns :few turns). The step-up/step-down effect of coil turn ratios in a transformer (Figure above) is analogous to gear tooth ratios in mechanical gear systems, transforming values of speed and torque in much the same way: (Figure below) Torque reducing gear train steps torque down, while stepping speed up.
